Fonte: Frost & Sullivan
From fields to tables: the importance of decarbonization of the food system
How innovation can reduce emissions of climate-related gases in food production and intensive livestock farming, which account for 26% of total global emissions
The food system has changed in recent years as the world’s population has grown and energy production and use have increased. In this context, decarbonizing the food system is also a crucial step to combat climate change and, as foreseen by the Paris climate agreements signed by 200 countries during COP21 of 2015, there is an increasing urgency to adopt sustainable practices in order to reduce the greenhouse gas emissions generated by the sector.
The environmental impact of global food systems
Improve nutrition and promote the adoption of sustainable agricultural practices to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from the sector
The world’s food systems - which include production and post-farming processes such as processing and distribution - contribute negatively to increasing the footprint of greenhouse gas emissions, accounting for over 26% of total global emissions. In the whole food chain, moreover, livestock and fish farming (often intensive) distinguishes themselves, as they are the largest contributors.
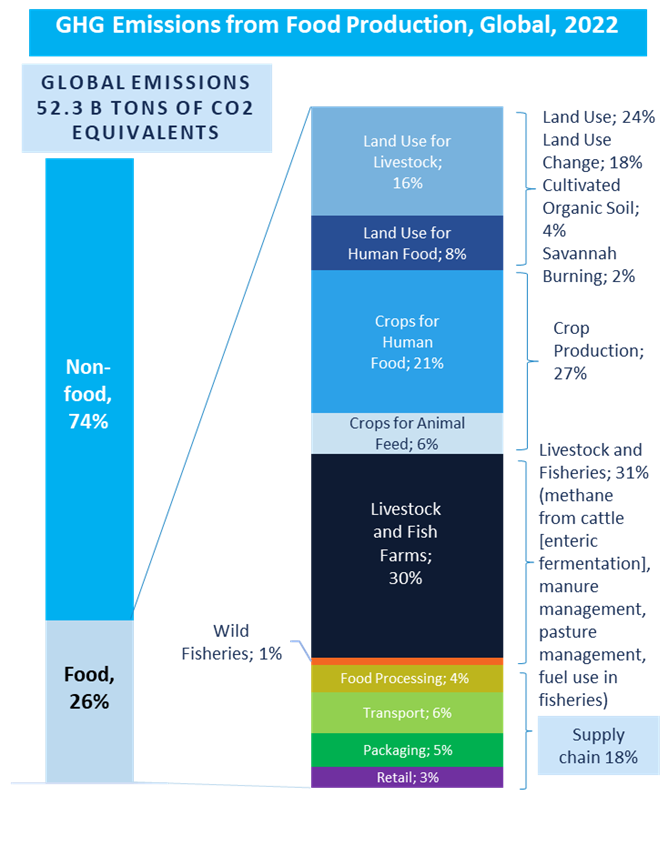

Per rendere i sistemi alimentari più resilienti e sostenibili nel lungo termine, come previsto dall’obiettivo 2 dell’Agenda 2030 dell’ONU denominato “Zero Hunger”, molti Paesi (non tutti) sono impegnati a migliorare la nutrizione e a promuovere pratiche agricole sostenibili.


In order to make food systems more resilient and sustainable in the long term, as called for by UN Agenda 2030 goal two called "Zero Hunger", many countries (not all) are committed to improving nutrition and promoting sustainable agricultural practices.
Why protein diversification is critical to developing a strategy that reduces reliance on intensive livestock farming
In this scenario, most national governments are considering protein diversification as a strategy to "build" food systems with reduced dependence on intensive livestock farming. For example, in 2023 the EU has announced an investment of half a billion euros to stimulate the development of innovative proteins by preparing the "European Protein Strategy".
Which are the growing alternatives to diversify protein supply
The protein-derived proteins from insects that are emerging as a source of animal feed are among the useful alternatives for diversifying the protein supply characterized by being in a growth phase, because of its particularly high nutritional efficiency and, at the same time, its low environmental impact.
Other alternative ingredients include plant-based proteins such as soya and cereals, with microbial proteins obtained through the fermentation of microorganisms - including fungi, yeasts and bacteria - representing a rapidly growing research field.
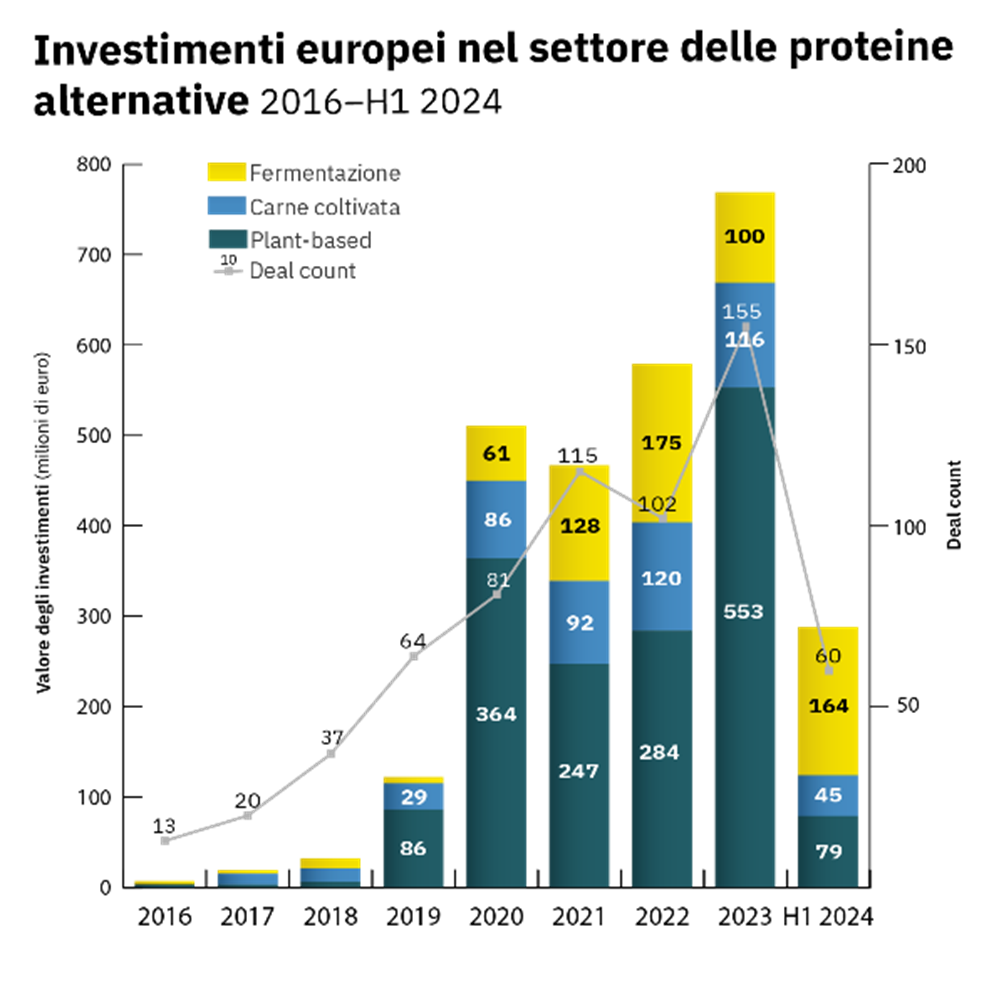

Fonte: Frost & Sullivan
The main challenges to be faced for the transition towards sustainable practices
Costs, consumers and the contrast to greenwashing
The main challenges in moving to sustainable practices are high initial costs for new technology purchases, infrastructure modernization and staff training. In addition, obtaining environmental certifications takes significant time and resources to meet the many standards required, further complicating the complexity of supply chains.
As far as consumers are concerned, the demand for sustainable products in the food sector is often variable, the shift to more environmentally friendly farming methodologies may result in lower land yields at an early stage as well as disruptions in the supply chain, The resulting difficulties in finding products and potential price increases for final consumers.
In this context, which combines needs and challenges, the risk of greenwashing arises, that is to say, declaring a commitment to sustainability as a façade, with the aim of adapting to a market trend and seizing its opportunities without adopting truly ecological practices, not only in the food sector. A phenomenon that is both regrettable and widespread, which determines the need to guarantee the traceability of the entire chain, starting from the production methods and the origin of raw materials.
How technology can make agriculture sustainable
Technological solutions for mitigation of emissions impacts start with agricultural monitoring measures, such as data collection technologies from drones, satellites, robots and sensors combined with artificial intelligence. This approach allows crop yields to be estimated, facilitates crop selection and makes better-informed decisions about plant health, growth stages, environmental conditions and pest presence, thus reducing the risks for farmers.
In soil monitoring, sensors and satellite imagery provide valuable information to analyze soil parameters such as moisture and nutrient content, while reducing water waste through intelligent irrigation systems. On the supply side, bio-fertilizers and bio-stimulants are the natural alternative to improve soil fertility.
How sustainable innovation can reduce environmental impact in other sectors through the circular economy
Agriculture is not the only sector to benefit from sustainable innovation. The developments and focus are on the valorization of food waste by intervening throughout the chain from collection, transport, sorting, recycling to final disposal. This approach is part of the circular economy paradigm, in which materials are reintroduced into production processes through reuse and recycling to generate value.
Switching to renewable energies, anaerobic digestion allows organic waste to be transformed into "clean" energy, thus enabling energy-efficient refrigeration. Finally, another particularly interesting area is intelligent packaging technologies, because they can prolong the shelf life of products and thus help to reduce food waste by packaging them with elements such as oxygen and moisture absorbers.
Decarbonising the agrifood system, the Report by Intesa Sanpaolo Innovation Center
Waste management is important to reduce food waste and utilise residues for compost or bioenergy production. Advanced chemical recycling, which produces alternative fuels, is also highlighted as essential.. Il Cross-Sector Report - Decarbonising the agrifood system, curated da Intesa Sanpaolo Innovation Center, explores innovative solutions and business models to decarbonise the agrifood supply chain, analysing Agriculture 4.0 technologies, and examines the use of renewable energy in this industry.
Do you need an overview of innovative solutions to decarbonise the agrifood supply chain?
Details of the emerging patterns are in the full report,
edited by Intesa Sanpaolo Innovation Center - Innovation Intelligence
