Which eco-sustainable materials to use in construction?
To face contemporary environmental challenges, there is a growing need to renew construction practices from a sustainable perspective, with innovative materials leading the transformation of a particularly polluting sector


After the crisis caused by the Covid-19 pandemic, the global economic recovery has pushed the construction market, recording a strong increase in construction activity, above all thanks to the substantial investments in infrastructure intended for the energy, transport and healthcare sectors. Furthermore, the economic and demographic growth of emergingmarkets is generating strong demand for construction materials in several countries such as China, India and Indonesia, with the United Arab Emirates and Saudi Arabia seeing an increase in construction activities as part of big projects. These countries are joined by Mexico and Brazil which, thanks to economic recovery combined with a "solid" internal demand, are recording an increase in construction activities.
In this context, on a global level the construction sector currently represents a market from 8 trillion dollars, which according to forecasts will grow further and reach 12,000 billion by 2028. However, currently The construction sector is characterized by a low environmental sustainability, as responsible for 40% of global energy consumption and of 39% of total CO2 emissions globally, of which 28% was due to the actual operation of the buildings for the activities of heating and cooling and the remaining 11% caused by traditional construction processes and the materials used.
Significant greenhouse gas emissions are also caused by production and transportation of materials such as cement - used on a large scale mainly due to the low cost compared to innovative and eco-sustainable solutions - which make the construction sector one of the most polluting globally.
Data makes it necessary to adopt a sustainable approach for the construction sector, which in addition to reducing CO2 emissions must face other problems relating to the sustainability of construction. For example, thanks to new technologies, sustainable construction also aims to reduce resource consumption and waste production. An unavoidable change driven by the need to reduce environmental impact, favored by new regulations for so-called "green buildings" and by greater awareness on a topic of crucial importance for the future of the Planet.
Today we are therefore looking for solutions for the design of efficient buildings by exploiting the new digital technologies, the adoption of practices typical of the paradigm ofcircular economy, as well as the use of eco-sustainable materials. Solutions that do not exclusively concern new constructions, with many countries having introduced incentives and regulations to promote it in recent years redevelopment of existing buildings as done by the European Union in approving the "green homes" directive.
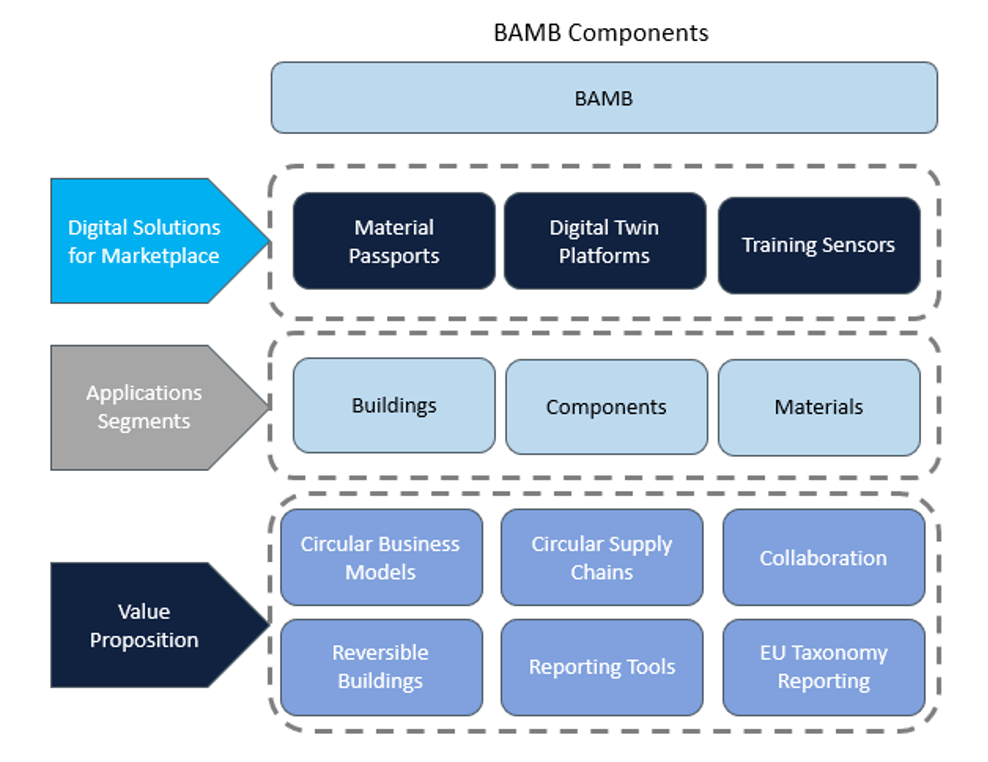
In this scenario, the choice of construction materials plays a fundamental role, as it influences the life cycle of individual buildings. Furthermore, strategies such as Building As Materials Banks (BAMB) go beyond the simple choice of using new eco-sustainable materials, by virtue of a circular approach who “treats” them building as reserves of reusable materials. This strategy, in fact, contributes to reducing the extraction of raw materials and the production of waste, transforming redevelopment into an opportunity to prolong the life of buildings, reduce their environmental impact and create added value for the community.

Eco-sustainable materials include, for example, the biobrick. Discovered in France, it is a sustainable building material made with a mix of hemp and a lime-based binder: rather than emitting it, the hemp captures CO2 from the atmosphere during its growth, with the biobrick also providing thermal and acoustic insulation, simultaneously regulating internal humidity both when used for new constructions and for the redevelopment of pre-existing buildings. A material that is also recyclable and reusable, thus fully falling within the paradigm of the circular economy.
Having given this example, it is necessary to underline how there are three categories of eco-sustainable materials that, in particular, stand out for their healthiness and good insulating properties: engineered wood, roofing and modular materials.
Engineered Wood
Engineered wood, also known as composite wood, is an innovative material made by joining layers of wood or other plant materials with adhesives. This type of wood is designed to offer greater strength and stability than solid wood, and also good thermal and acoustic insulation properties as well as a wide range of possible applications including load-bearing structures, floors, cladding and furniture.
Roofing materials
Roofs protect buildings from atmospheric agents, such as rain, wind and sun. Among the technological solutions that are emerging there are solar tiles that combine the functions of roofing and solar energy production, recycled metal tiles, fiber cement tiles and vegetated roofs.
Modular Materials
Prefabricated modular materials are lightweight, easy-to-install components used to build structures such as panels and drywall and ceiling systems. These materials offer numerous advantages, including reduced construction and disposal times. For example, Plant Prefab - a Californian company active in the construction of modular homes - uses cellulose fiber obtained from recycled paper. Furthermore, among innovative eco-sustainable materials we can mention rock wool, glass wool, cork, sugar canes, ecological paints - less polluting and healthier than traditional ones - and sustainable concrete.
In conclusion, innovative eco-sustainable materials represent one of the keys to an environmentally friendly future of construction since, when adopted, they also improve energy efficiency. An opportunity for the transformation of the sector which, thanks to the use of these materials and sustainable practices, can drastically reduce polluting emissions and thus have a positive impact on the future of our planet.
