If you want to have a complete overview of new nuclear technologies
Details in the report
curated by Intesa Sanpaolo Innovation Center - Innovation Intelligence
The Return of New Nuclear Energy
What Innovations and Prospects Lie Ahead for the Future of Energy?
Given the urgency of meeting the growing demand for energy and as a complementary solution to renewable energy sources for electricity generation, nuclear power is regaining global attention. This shift is driven by the need to achieve net-zero goals by 2050. Projections suggest that by 2035, low greenhouse gas emission sources could account for up to 77% of the global energy mix, rising to 89% when nuclear power is included. While nuclear energy dates back to the 20th century and has historically been linked to safety concerns, advancements in nuclear technology over the past 70 years warrant a fresh perspective.

Can Nuclear Power Be Strategic for Italy?
In recent years, Italy has paused domestic industrial nuclear production due to concerns over operational risks and radioactive waste management. However, research and international collaborations have continued. The energy landscape is evolving rapidly. Italy is paving the way for its first publicly-driven energy company, with Enel expected to hold a 51% majority stake, followed by Ansaldo Nucleare (39%) and Leonardo (10%). Within this framework, the startup Newcleo has drawn the attention of around 700 investors and achieved unicorn status with a valuation of €1.3 billion.
The Momentum of Investments
Investments in nuclear technology are on the rise, attracting major tech companies. For instance, Google recently partnered with Kairos Power to develop a molten salt reactor, while Microsoft is collaborating with Constellation Energy to revive an existing nuclear power plant.
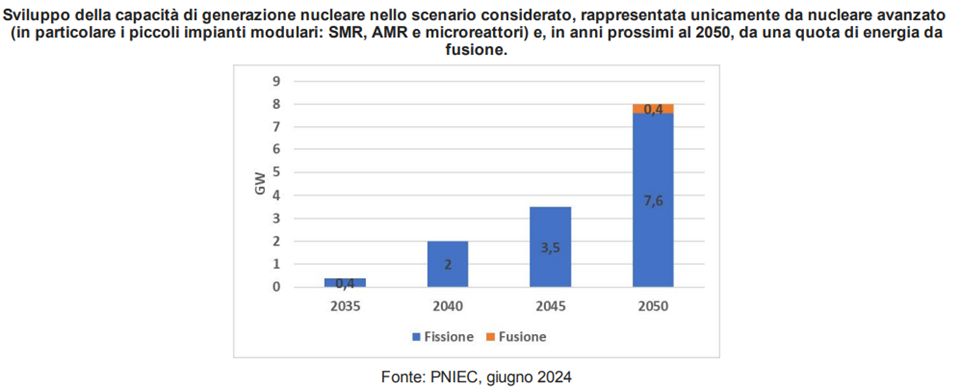
In Italy, the 2024 Mission Innovation Decree allocated €135 million to research compact modular reactors (SMRs) and nuclear fusion. Moreover, on July 1, 2024, the final version of the Integrated National Energy and Climate Plan (PNIEC) was submitted to the European Commission. The plan aims to harness nuclear fission-based power generation by 2035 and to explore nuclear fusion starting in 2050.


What Are the Current Cutting-Edge Technologies?
New technologies aim not only to enhance efficiency and safety but also to reduce costs. Innovations include advanced fission reactors, such as fourth-generation reactors (AMRs) and compact modular reactors (SMRs). Another emerging area is the production of pink hydrogen using nuclear energy. Additionally, solutions for minimizing the environmental impact of radioactive waste are being developed.
Fourth-Generation Reactors (AMRs) and Compact Modular Reactors (SMRs)
Fourth-generation AMRs bring advancements like gas-cooled systems using liquid lead or molten salts, which reduce operational risks and improve fuel management. SMRs, on the other hand, address challenges posed by third-generation nuclear plants. Their compact design ensures greater safety and reduced costs. These reactors offer modular, scalable, and customizable solutions to meet specific energy needs, making them suitable for decentralized setups.
Nuclear Hydrogen
Hydrogen is vital for industries that cannot easily transition to electrification, such as heavy transport and sectors requiring rapid refueling and autonomy. While traditionally produced using fossil fuels, hydrogen can now be generated using nuclear technology. The heat produced by nuclear reactors can split water molecules, enabling sustainable hydrogen production.
Radioactive Waste Management
Effective radioactive waste management involves classifying waste into four categories based on its radioactivity level, each requiring tailored treatment and disposal methods. Artificial intelligence (AI) is playing a growing role in automating waste sorting and monitoring.
Innovative techniques include plasma incineration, which transforms waste into reusable vitrified materials, and wet oxidation, which degrades contaminants into less toxic compounds. For liquid waste, chemical cementation is emerging as a reliable method. Long-term waste treatment technologies, such as pyrolysis and bioremediation, use thermochemical and biological processes to restore contaminated environments.
New Nuclear Energy, a report by Intesa Sanpaolo Innovation Center
Nuclear power has undergone significant advancements, offering state-of-the-art technologies while facing challenges such as stringent regulations and high costs.. The Industry Trends Report - Nuclear Power: The Future of Nuclear Energy, curated by Intesa Sanpaolo Innovation Center, analyzes the different technologies that can be used to address these challenges.
