Security of Things, the Trend Analysis and Applied Research report by Intesa Sanpaolo Innovation Center
Trend Analysis and Applied Research of Intesa Sanpaolo Innovation Center deals with detecting and analyzing technological and industrial innovation trends, editing reports and publications in collaboration with the internal research and development laboratories dedicated to artificial intelligence and neuroscience and with scientific partners of high value.
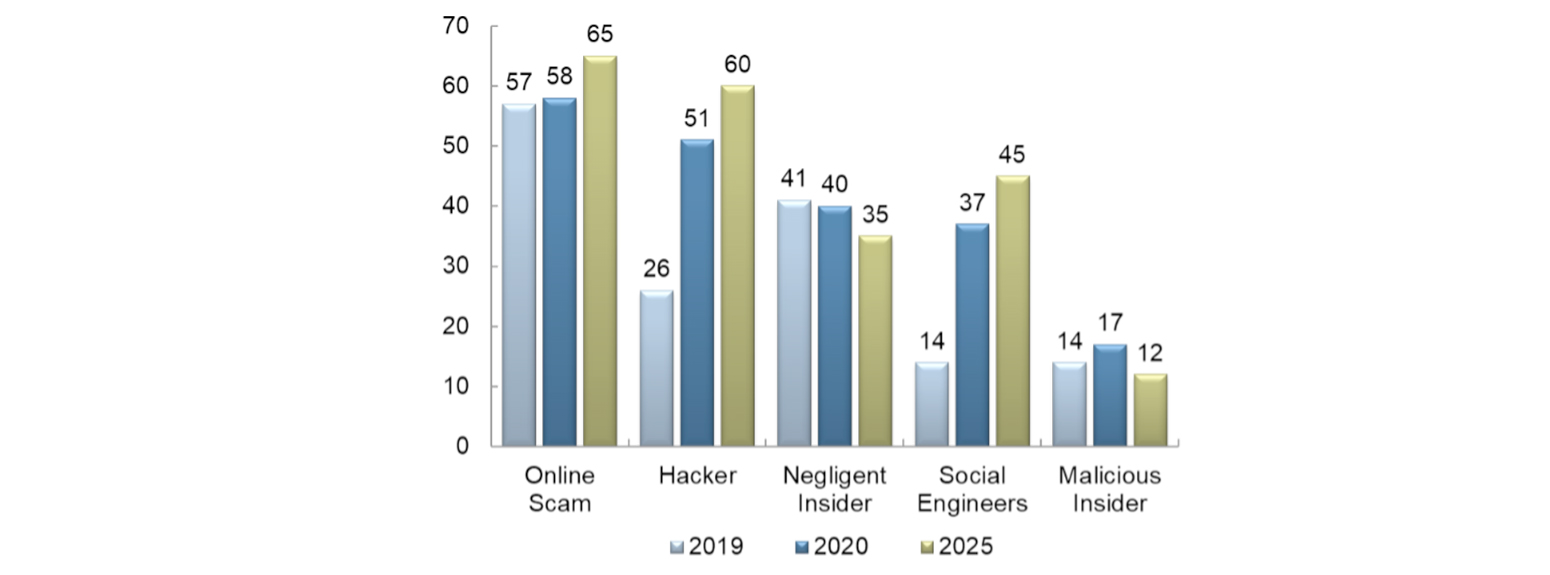
On the subject of IT security, one of the latest reports produced by Trend Analysis and Applied Research is Security of Things dedicated to the increase in risks due to the growing number of cyber attacks. The report analyzes emerging threats in IoT and highlights responses from the industrial, healthcare and automotive sectors, explaining both long-term and short-term strategies used to address cyber attacks.